|
|
3 years ago | |
|---|---|---|
| 0-intro-jupyter | 3 years ago | |
| 1-ml-landscape | 3 years ago | |
| 2-linear-regressor | 3 years ago | |
| slides | 3 years ago | |
| .gitignore | 3 years ago | |
| Readme.md | 3 years ago | |
| aiVsML.png | 3 years ago | |
| diff.png | 3 years ago | |
Readme.md
Introduction
Building an AI system is a careful process of reverse-engineering human traits and capabilities in a machine1:
-
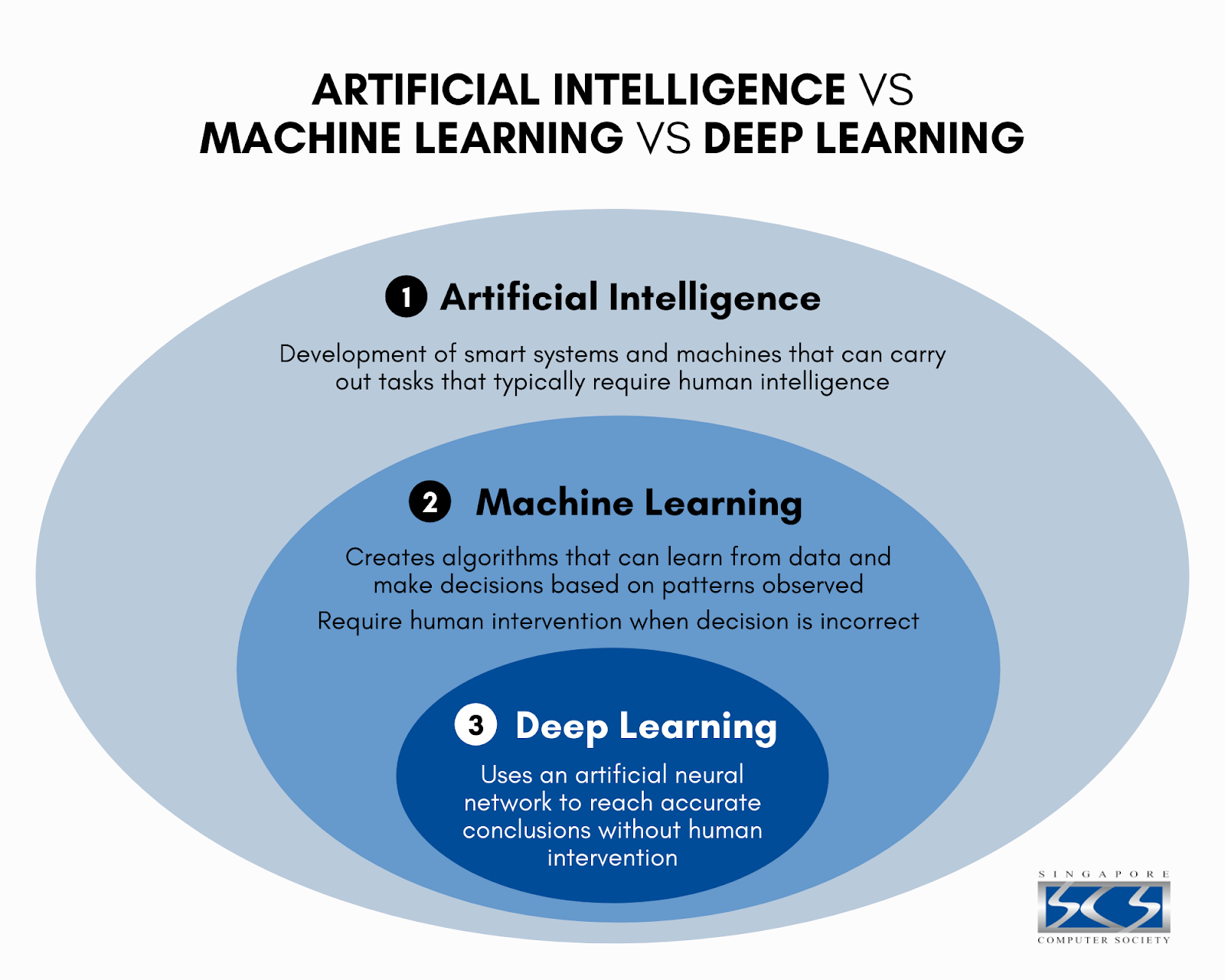
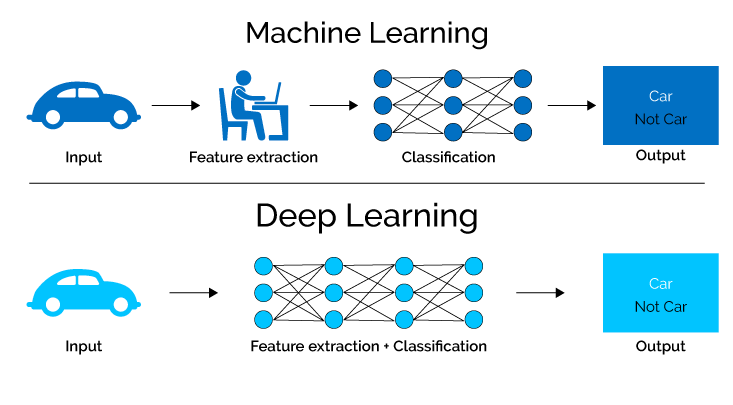
Machine Learning: ML teaches a machine how to make inferences and decisions based on past experience. It identifies patterns and analyses past data to infer the meaning of these data points to reach a possible conclusion without having to involve human experience.
-
Deep Learning: Deep Learning is an ML technique. It teaches a machine to process inputs through layers in order to classify, infer and predict the outcome.
-
Neural Networks: Neural Networks work on similar principles to Human Neural cells. They are a series of algorithms that captures the relationship between various underlying variables and processes the data as a human brain does.
-
Natural Language Processing: NLP is the science of reading, understanding, and interpreting a language by a machine. Once a machine understands what the user intends to communicate, it responds accordingly.
-
Computer Vision: Computer vision algorithms try to understand an image by breaking down an image and studying different parts of the object. This helps the machine classify and learn from a set of images to make a better output decision based on previous observations.
-
Cognitive Computing: Cognitive computing algorithms try to mimic a human brain by analyzing text/speech/images/objects in a manner that a human does and tries to give the desired output. Also, take up applications of artificial intelligence courses for free.
Sillabus
- Introduction to Python programming and Google Colab
- A Landscape to machine learning: learning from real data
- Linear and Logistic Regressors
- Artificial Neural Networks
Introduction to python
Landscape to machine learning
Linear Regressor
Logistic Regressor
Artificial Neural Network
by Gerardo Marx June 2023
-
https://www.mygreatlearning.com/blog/what-is-artificial- intelligence/ ↩︎