You cannot select more than 25 topics
Topics must start with a letter or number, can include dashes ('-') and can be up to 35 characters long.
|
|
2 years ago | |
|---|---|---|
| main_files | 2 years ago | |
| Readme.md | 2 years ago | |
| main.ipynb | 2 years ago | |
Readme.md
from sklearn import datasets
iris = datasets.load_iris()
print(iris.DESCR)
.. _iris_dataset:
Iris plants dataset
--------------------
**Data Set Characteristics:**
:Number of Instances: 150 (50 in each of three classes)
:Number of Attributes: 4 numeric, predictive attributes and the class
:Attribute Information:
- sepal length in cm
- sepal width in cm
- petal length in cm
- petal width in cm
- class:
- Iris-Setosa
- Iris-Versicolour
- Iris-Virginica
:Summary Statistics:
============== ==== ==== ======= ===== ====================
Min Max Mean SD Class Correlation
============== ==== ==== ======= ===== ====================
sepal length: 4.3 7.9 5.84 0.83 0.7826
sepal width: 2.0 4.4 3.05 0.43 -0.4194
petal length: 1.0 6.9 3.76 1.76 0.9490 (high!)
petal width: 0.1 2.5 1.20 0.76 0.9565 (high!)
============== ==== ==== ======= ===== ====================
:Missing Attribute Values: None
:Class Distribution: 33.3% for each of 3 classes.
:Creator: R.A. Fisher
:Donor: Michael Marshall (MARSHALL%PLU@io.arc.nasa.gov)
:Date: July, 1988
The famous Iris database, first used by Sir R.A. Fisher. The dataset is taken
from Fisher's paper. Note that it's the same as in R, but not as in the UCI
Machine Learning Repository, which has two wrong data points.
This is perhaps the best known database to be found in the
pattern recognition literature. Fisher's paper is a classic in the field and
is referenced frequently to this day. (See Duda & Hart, for example.) The
data set contains 3 classes of 50 instances each, where each class refers to a
type of iris plant. One class is linearly separable from the other 2; the
latter are NOT linearly separable from each other.
|details-start|
**References**
|details-split|
- Fisher, R.A. "The use of multiple measurements in taxonomic problems"
Annual Eugenics, 7, Part II, 179-188 (1936); also in "Contributions to
Mathematical Statistics" (John Wiley, NY, 1950).
- Duda, R.O., & Hart, P.E. (1973) Pattern Classification and Scene Analysis.
(Q327.D83) John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 0-471-22361-1. See page 218.
- Dasarathy, B.V. (1980) "Nosing Around the Neighborhood: A New System
Structure and Classification Rule for Recognition in Partially Exposed
Environments". IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine
Intelligence, Vol. PAMI-2, No. 1, 67-71.
- Gates, G.W. (1972) "The Reduced Nearest Neighbor Rule". IEEE Transactions
on Information Theory, May 1972, 431-433.
- See also: 1988 MLC Proceedings, 54-64. Cheeseman et al"s AUTOCLASS II
conceptual clustering system finds 3 classes in the data.
- Many, many more ...
|details-end|
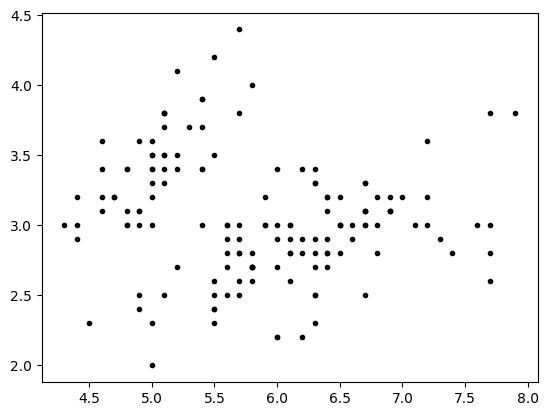
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
sl = iris.data[:,0:1]
sw = iris.data[:,1:2]
plt.plot(sl,sw, '.k')
plt.show()
iris.target
array([0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2,
2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2,
2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2])
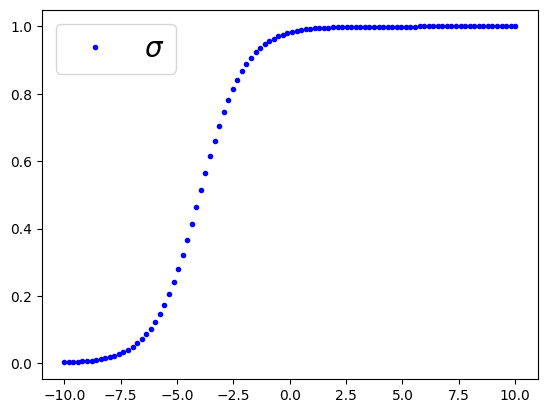
Decision boundaries
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
t = np.linspace(-10,10, 100)
sig = 1/(1+np.exp(-t-4))
plt.plot(t,sig, '.b', label=r"$\sigma$")
plt.legend(loc='upper left', fontsize =20)
plt.show()
Iris-Setosa Classifier based on petal width
X = iris.data[:,3:4]
y = (iris.target == 0).astype(int)
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
mylr = LogisticRegression(solver='lbfgs', random_state=42)
mylr.fit(X,y)
LogisticRegression(random_state=42)In a Jupyter environment, please rerun this cell to show the HTML representation or trust the notebook.
On GitHub, the HTML representation is unable to render, please try loading this page with nbviewer.org.
LogisticRegression(random_state=42)
Xnew = np.linspace(-1,3,100).reshape(-1,1)
yPred = mylr.predict_proba(Xnew)
#plt.plot(Xnew,yPred[:,0], label='No Iris')
plt.plot(Xnew,yPred[:,1], label='Yes Iris')
plt.legend()
plt.plot(X,y,'og')
plt.show()
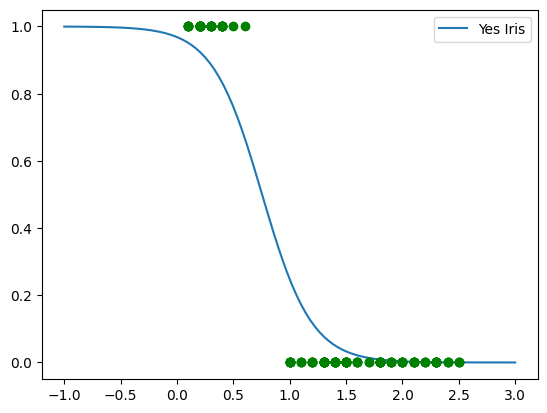
Iris-Setosa petal length
X = iris.data[:,2:3]
y = (iris.target == 0).astype(int)
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
mylr = LogisticRegression(solver='lbfgs', random_state=42)
mylr.fit(X,y)
LogisticRegression(random_state=42)In a Jupyter environment, please rerun this cell to show the HTML representation or trust the notebook.
On GitHub, the HTML representation is unable to render, please try loading this page with nbviewer.org.
LogisticRegression(random_state=42)
Xnew = np.linspace(0,8,100).reshape(-1,1)
yPred = mylr.predict_proba(Xnew)
#plt.plot(Xnew,yPred[:,0], label='No Iris')
plt.plot(Xnew,yPred[:,1], label='Yes Iris')
plt.legend()
plt.plot(X,y,'og')
plt.axis([1.5, 5, -0.1, 1.1])
plt.show()
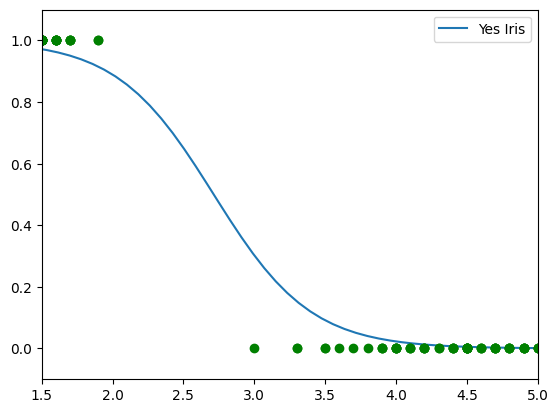
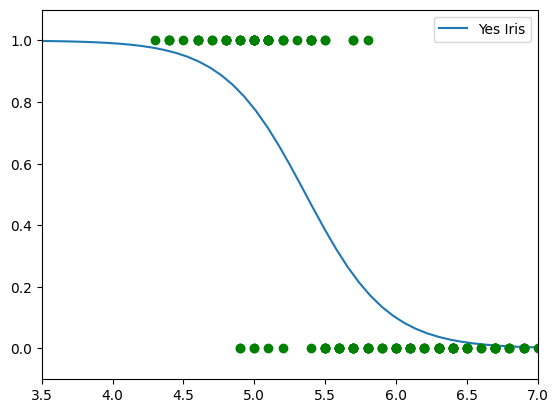
Iris-Setosa Sepal-Length
X = iris.data[:,0:1]
y = (iris.target == 0).astype(int)
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
mylr = LogisticRegression(solver='lbfgs', random_state=42)
mylr.fit(X,y)
LogisticRegression(random_state=42)In a Jupyter environment, please rerun this cell to show the HTML representation or trust the notebook.
On GitHub, the HTML representation is unable to render, please try loading this page with nbviewer.org.
LogisticRegression(random_state=42)
Xnew = np.linspace(0,8,100).reshape(-1,1)
yPred = mylr.predict_proba(Xnew)
#plt.plot(Xnew,yPred[:,0], label='No Iris')
plt.plot(Xnew,yPred[:,1], label='Yes Iris')
plt.legend()
plt.plot(X,y,'og')
plt.axis([3.5, 7, -0.1, 1.1])
plt.show()
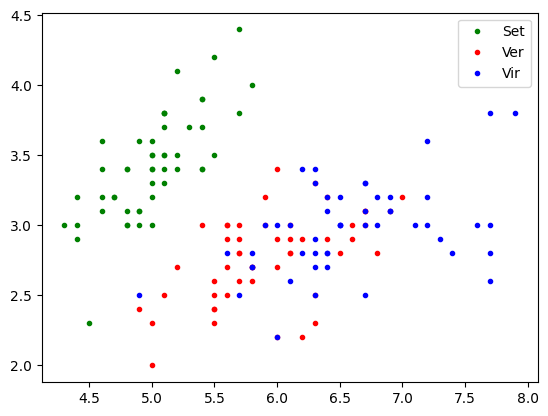
Multiple features classifier
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
sl = iris.data[:,0:1]
sw = iris.data[:,1:2]
tg = iris.target
plt.plot(sl[tg==0,0], sw[tg==0,0],'.g' ,label='Set')
plt.plot(sl[tg==1,0], sw[tg==1,0],'.r', label='Ver')
plt.plot(sl[tg==2,0], sw[tg==2,0],'.b', label='Vir')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
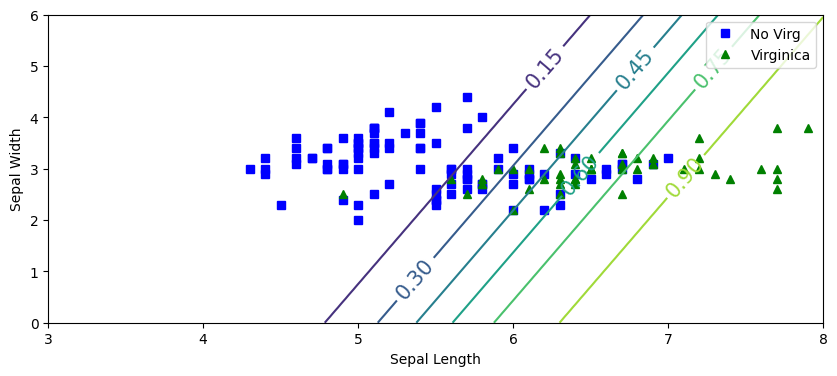
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
X = iris.data[:,0:2]
y = (iris.target==2).astype(int)
mylrvir = LogisticRegression(
random_state=22,
tol=1e-5,
C=100,
max_iter=100,
solver='newton-cg'
)
mylrvir.fit(X,y)
LogisticRegression(C=100, random_state=22, solver='newton-cg', tol=1e-05)In a Jupyter environment, please rerun this cell to show the HTML representation or trust the notebook.
On GitHub, the HTML representation is unable to render, please try loading this page with nbviewer.org.
LogisticRegression(C=100, random_state=22, solver='newton-cg', tol=1e-05)
import numpy as np
x0, x1 = np.meshgrid(
np.linspace(3,8,100).reshape(-1,1),
np.linspace(0,6,100).reshape(-1,1)
)
Xnew = np.c_[x0.ravel(), x1.ravel()]
yPred = mylrvir.predict_proba(Xnew)
plt.figure(figsize=(10,4))
plt.plot(X[y==0,0], X[y==0,1],'bs',label='No Virg')
plt.plot(X[y==1,0], X[y==1,1],'g^',label='Virginica')
zz=yPred[:,1].reshape(x0.shape)
contour=plt.contour(x0,x1,zz)
plt.clabel(contour, inline=1,fontsize=15)
plt.xlabel("Sepal Length")
plt.ylabel("Sepal Width")
plt.legend()
plt.show()
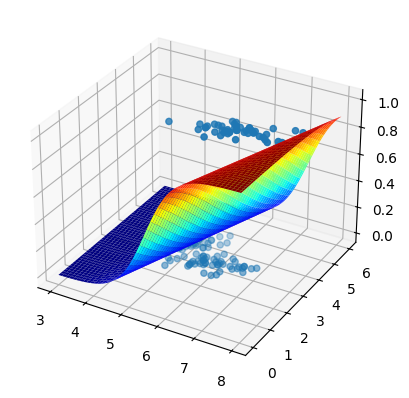
fig, ax =plt.subplots(subplot_kw={"projection": "3d"})
surf = ax.plot_surface(x0,x1,zz, cmap='jet')
ax.scatter(iris.data[:,0:1], iris.data[:,1:2], y, 'or')
<mpl_toolkits.mplot3d.art3d.Path3DCollection at 0x16c24cda0>
Multiple features and muticlass classifier
X = iris.data[:,0:2]
y = iris.target
lrmc = LogisticRegression(
multi_class='multinomial',
solver='lbfgs',
C=100,
random_state=22
)
lrmc.fit(X,y)
LogisticRegression(C=100, multi_class='multinomial', random_state=22)In a Jupyter environment, please rerun this cell to show the HTML representation or trust the notebook.
On GitHub, the HTML representation is unable to render, please try loading this page with nbviewer.org.
LogisticRegression(C=100, multi_class='multinomial', random_state=22)
y
array([0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2,
2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2,
2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2])
import numpy as np
x0, x1 = np.meshgrid(
np.linspace(3,8,100).reshape(-1,1),
np.linspace(0,6,100).reshape(-1,1)
)
Xnew = np.c_[x0.ravel(), x1.ravel()]
yPred = lrmc.predict_proba(Xnew)
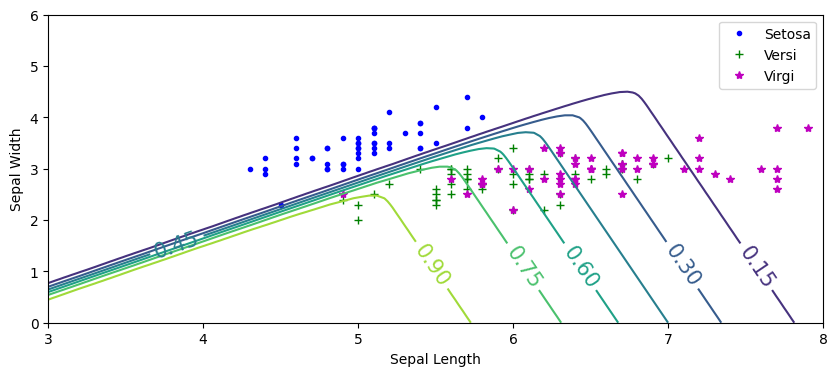
plt.figure(figsize=(10,4))
plt.plot(X[y==0,0], X[y==0,1],'.b',label='Setosa')
plt.plot(X[y==1,0], X[y==1,1],'+g',label='Versi')
plt.plot(X[y==2,0], X[y==2,1],'*m',label='Virgi')
zz=yPred[:,1].reshape(x0.shape)
contour=plt.contour(x0,x1,zz)
plt.clabel(contour, inline=1,fontsize=15)
plt.xlabel("Sepal Length")
plt.ylabel("Sepal Width")
plt.legend()
plt.show()
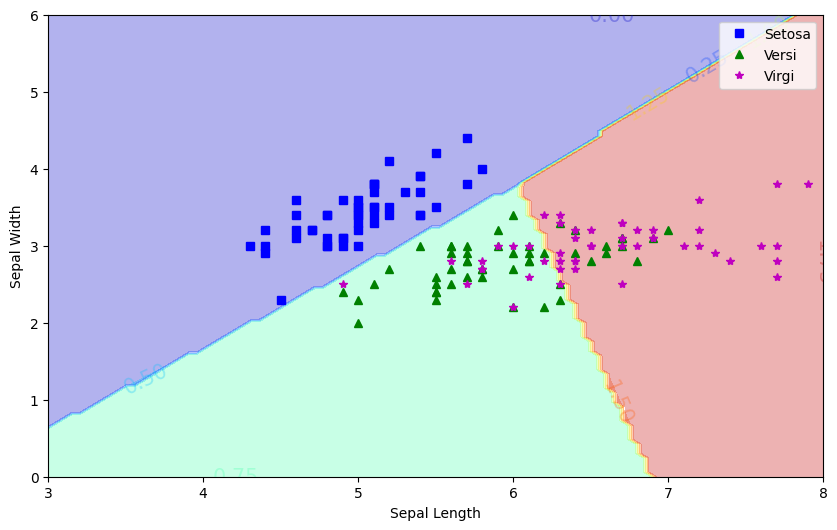
yPred = lrmc.predict(Xnew)
plt.figure(figsize=(10,6))
plt.plot(X[y==0,0], X[y==0,1],'bs',label='Setosa')
plt.plot(X[y==1,0], X[y==1,1],'g^',label='Versi')
plt.plot(X[y==2,0], X[y==2,1],'*m',label='Virgi')
zz=yPred.reshape(x0.shape)
contour=plt.contourf(x0,x1,zz, cmap='jet', alpha=0.3)
plt.clabel(contour, inline=1,fontsize=15)
plt.xlabel("Sepal Length")
plt.ylabel("Sepal Width")
plt.legend()
plt.show()
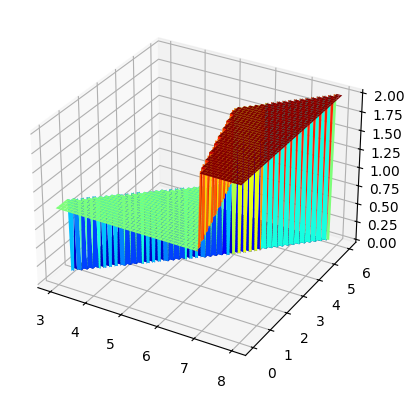
fig, ax =plt.subplots(subplot_kw={"projection": "3d"})
surf = ax.plot_surface(x0,x1,zz, cmap='jet')
#ax.scatter(iris.data[:,0:1], iris.data[:,1:2], y, 'or')