|
|
3 weeks ago | |
|---|---|---|
| C-MAG.png | 4 weeks ago | |
| CTR-commands.pdf | 3 weeks ago | |
| CTlaser-manual.pdf | 3 weeks ago | |
| DCPower.png | 4 weeks ago | |
| DMM4040.png | 3 weeks ago | |
| Dibujo.png | 4 weeks ago | |
| Multimeter.png | 4 weeks ago | |
| Pyrometer.png | 4 weeks ago | |
| README.md | 3 weeks ago | |
| SystemDC.png | 4 weeks ago | |
| Tabla-comandos-pyrometer.PNG | 3 weeks ago | |
| Table-Emissivity.PNG | 3 weeks ago | |
| ni-visa_19.5_online_repack3.rar | 3 weeks ago | |
README.md
Monitoring of Electrical and Thermal Parameters in a Metal Part
Introduction
This project aims to implement a data acquisition system for measuring temperature, voltage, and current in a metal part subjected to constant current, with the purpose of analyzing its electrical and thermal behavior in real time.
Methodology
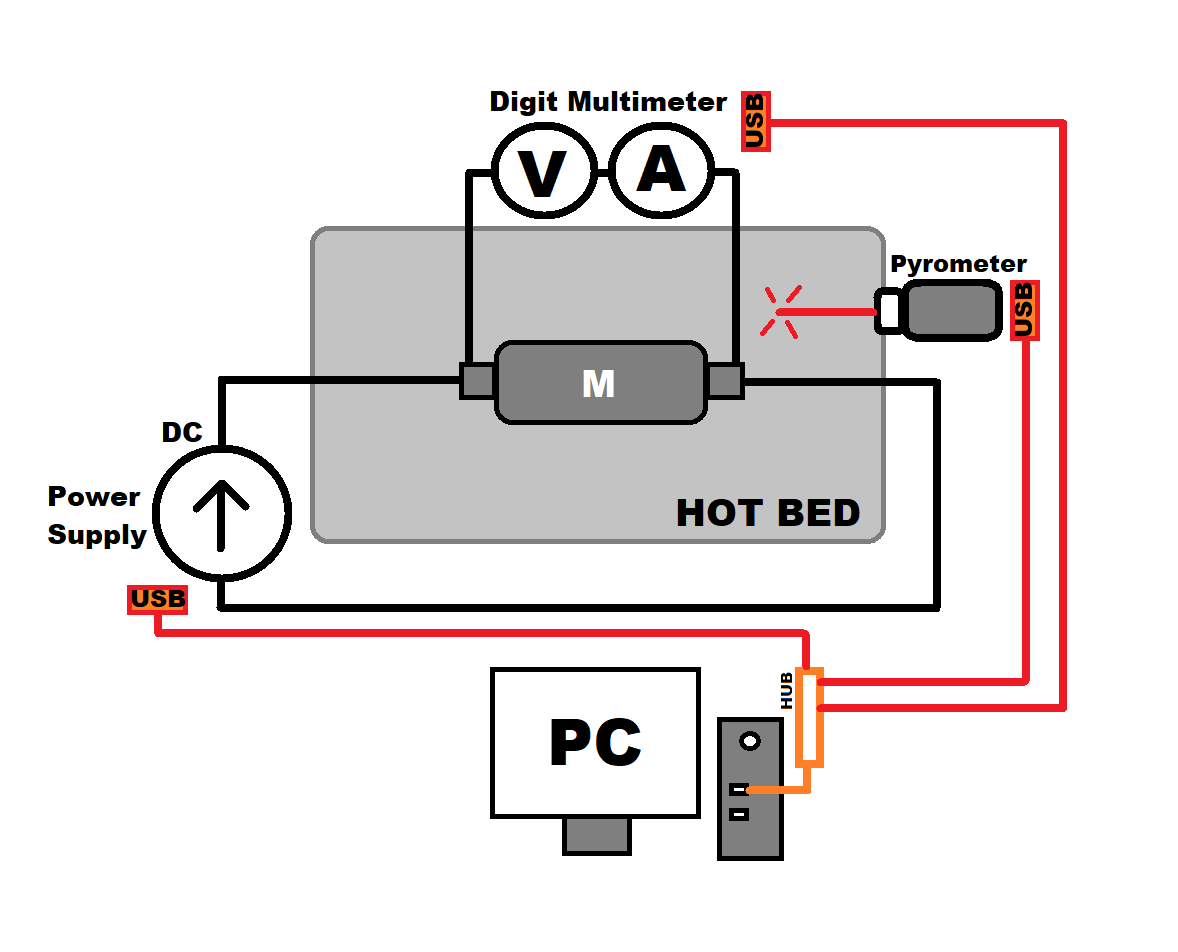
Representative drawing
The image shows the parts that make up the experiment.
Equipment
Communication
Communication with Digit Multimeter M3500A and System DC Power Supply 150 V / 10 A
To communicate the Digit Multimeter M3500A and the System DC Power Supply 150 V / 10 A a USB cable was used through the VISA protocol (Virtual Instrument Software Architecture) which is a standard for configuring, programming and debugging instrumentation systems that include GPIB interfaces. To do this, you first have to download the NI-VISA software on the computer you intend to use since Python is used to communicate through the Python wrapper pyvisa which requires the real VISA installation on the system. Otherwise an error will be thrown.
It is installed pyvisa:
pip install pyvisa
To find out if Pyvisa detects the instruments, run the following code in Python:
import pyvisa
rm = pyvisa.ResourceManager()
print(rm.list_resources())
If a series of codes are displayed in the Terminal, it means the instruments have indeed been detected and are responding with their data. Something like this:
'USB0::0x164E::0x0DAD::TW00013644::INSTR'
Communication with the Optris CTlaser pyrometer OPTCTLLTSF
Communication with the Optris CTlaser pyrometer was performed using the sensor's native binary protocol, using the Python programming language and the standard pyserial library for access to the COM port (virtual USB RS-232).
The sensor protocol consists of sending single-byte binary commands and receiving two-byte encoded responses, representing data such as temperature in uint16 format.
Libraries used:
import serial
import time
| communication parameters | |
|---|---|
| Baudrate | 115200 bps |
| Bits de datos | 8 |
| Paridad | Ninguna |
| Bits de parada | 1 |
| Timeout | 1 segundo |
Command to get temperature
COMANDO_TEMPERATURA = bytes([0x01])
This command requests the process temperature (Tprocess). The sensor's response is 2 bytes, which must be interpreted using the following formula:
temperatura = ((byte1 * 256 + byte2) - 1000) / 10
All this information was obtained from the manufacturer's manuals which are attached to this repository. CTR-commands and CTlaser-manual
Minimum code for pyrometer reading
import serial
import time
sensor = serial.Serial('COM9', baudrate=9600, timeout=1)
time.sleep(2)
sensor.write(bytes([0x01])) #Comando para solicitar la temperatura
time.sleep(0.2)
respuesta = sensor.read(2)
if len(respuesta) == 2:
byte1, byte2 = respuesta[0], respuesta[1]
temperatura = ((byte1 * 256 + byte2) - 1000) / 10
print(f"Temperatura: {temperatura:.1f} °C")
else:
print("No se recibió respuesta válida.")
sensor.close()
Communication with Digit Multimeter Tektronix DMM4040
Para poder establecer comunicación entre el multímetro digital Tektronix DMM4040 y la computadora mediante una interfaz RS-232, utilizando Python y la librería Pyvisa. La comunicación se realiza por comandos SCPI (Standar Commands for Programmable Instruments), ampliamente utilizados en istrumentación electrónica.
Para poder comunicarnos con el multimetro es necesario tener un cable serial RS-232 a USB (adaptador compatible, ejemplo: PL2303, CH340, FTDI) y conectarlo tanto a la salida de datos serial del multimetro digital DMM4040 como a un puerto USB disponible en el computador, también, es necesario tener instalado el software de NI_VISA (Controlador requerido para comunicación serial por PyVISA), Python e instalar la librería pyvisa.
Código de ejemplo para conectar el multimetro DMM4040 con pyhton
import pyvisa
import time
# Crear administrador VISA
rm = pyvisa.ResourceManager()
puerto = 'ASRL16::INSTR' # Asegurarse que este valor coincida con NI MAX
try:
multimetro = rm.open_resource(puerto)
# Configuración de la interfaz RS-232
multimetro.baud_rate = 9600
multimetro.data_bits = 8
multimetro.parity = pyvisa.constants.Parity.none
multimetro.stop_bits = pyvisa.constants.StopBits.one
multimetro.flow_control = pyvisa.constants.ControlFlow.none
multimetro.timeout = 5000
multimetro.write_termination = '\r\n'
multimetro.read_termination = '\r\n'
# Configurar medición de corriente DC (puedes usar VOLT:DC para voltaje)
multimetro.write("*CLS")
multimetro.write("CONF:CURR:DC")
multimetro.write("VOLT:DC:NPLC 1")
multimetro.write("TRIG:SOUR IMM")
multimetro.write("TRIG:DEL 0")
multimetro.write("SAMP:COUN 1")
# Iniciar y obtener la lectura
multimetro.write("INIT")
lectura = multimetro.query("FETCH?")
primera_lectura = lectura.strip().split(',')[0]
print("Corriente medida (DC):", primera_lectura, "A")
except Exception as e:
print("Error en la comunicación con el multímetro:", str(e))